Kalopanaxsaponin B inhibits LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting IRAK1 Kinase.
Eun-Ha Joh, Jin-Ju Jeong, Dong-Hyun Kim
文献索引:Cell. Immunol. 279(1) , 103-8, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The stem bark of Kalopanax pictus Nakai (KP, family Araliaceae), of which main constituent is kalopanaxsaponin B, has been used for inflammation in Chinese traditional medicine. We isolated kalopanaxsaponin B from KP and investigated its anti-inflammatory effect in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated peritoneal macrophages and on LPS-stimulated systemic inflammation in male ICR mice. Kalopanaxsaponin B inhibited the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-stimulated peritoneal macrophages. Kalopanaxsaponin B also inhibited the activation of IRAK1, IKK-β, NF-κB and MAP kinases (ERK, JNK, p-38). Treatment with LPS in the presence of kalopanaxsaponin B inhibited LPS-induced IRAK1 degradation and phosphorylation. Kalopanaxsaponin B inhibited IRAK1 kinase binding activity. However, kalopanaxsaponin B did not inhibit the NF-κB activation in active IKK-β-transfected macrophages. Kalopanaxsaponin B did not inhibit the binding of LPS on toll-like receptor-4 of the macrophages. Kalopanaxsaponin B inhibited LPS-induced systemic inflammation in mice. Based on these findings, kalopanaxsaponin B ameliorates LPS-induced systemic inflammation by inhibiting IRAK1 kinase.Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Inc.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
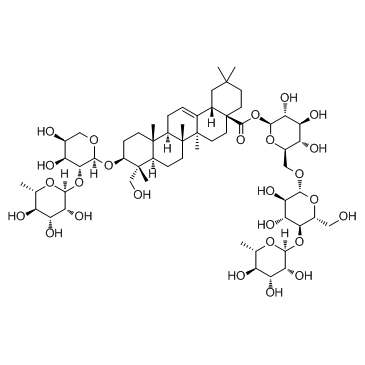 |
常春藤苷C; 常春藤皂苷C
CAS:14216-03-6 |
C59H96O26 |
|
[Studies on the saponin constituents of Kalopanax septemlobu...
1990-01-01 [Yao Xue Xue Bao 25(1) , 29-34, (1990)] |
|
Triterpenoidal saponins from the bark of Kalopanax pictum va...
1991-03-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 14(1) , 19-24, (1991)] |
|
Antinociceptive and anti-rheumatoidal effects of Kalopanax p...
2002-02-01 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 79(2) , 199-204, (2002)] |
|
Kalopanaxsaponin A from Kalopanax pictus, a potent antioxida...
2002-01-01 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 79(1) , 113-8, (2002)] |
|
Kalopanaxsaponins A and B isolated from Kalopanax pictus ame...
2012-04-01 [Phytother Res. 26(4) , 546-51, (2012)] |