Thermodynamic properties of nucleotide-free EF-Tu from Thermus thermophilus in the presence of low-molecular weight effectors of its GTPase activity.
Erik Sedlák, Gabriel Zoldák, Marián Antalík, Mathias Sprinzl
文献索引:Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1597(1) , 22-7, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The thermal transition of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus thermophilus in the presence of low-molecular weight effectors was studied by differential scanning calorimetry. The effectors of GTPase activity used were the antibiotic kirromycin and the cations Li(+), Na(+), K(+) and NH(4)(+) in the chloride form. The temperature of thermal denaturation and the cooperativity of the transition of nucleotide-free EF-Tu (EF-Tu(f)) in the presence of kirromycin are comparable with those of the EF-Tu x guanosine-5'-[beta,gamma-imido]triphosphate (GppNHp) form, indicating similar conformational states. Increased concentrations of Na(+) and K(+) stabilized EF-Tu(f) in a manner similar to GppNHp. NH(4)(+) decreased the transition temperature of EF-Tu(f) and Li(+) decreased both the temperature and the calorimetric enthalpy of the thermal transition of EF-Tu(f). In the presence of salts, binding of kirromycin had a stabilizing effect on EF-Tu(f). Correlation between the GTPase activity and thermodynamic characteristics of EF-Tu(f) induced by kirromycin in the absence or presence of the cations is discussed.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
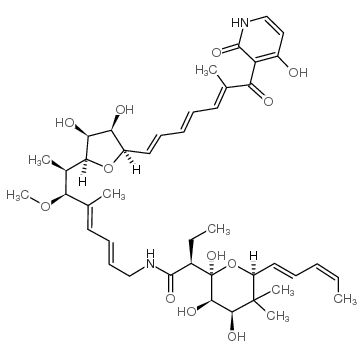 |
Mocimycin
CAS:50935-71-2 |
C43H60N2O12 |
|
A signal relay between ribosomal protein S12 and elongation ...
2009-02-01 [RNA 15(2) , 208-14, (2009)] |
|
The phosphopantetheinyl transferase KirP activates the ACP a...
2011-06-01 [FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 319(1) , 26-33, (2011)] |
|
Inhibitory mechanisms of antibiotics targeting elongation fa...
2002-02-01 [Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 3(1) , 121-31, (2002)] |
|
G13A substitution affects the biochemical and physical prope...
2002-01-15 [Biochemistry 41(2) , 628-33, (2002)] |
|
The kirromycin gene cluster of Streptomyces collinus Tü 365 ...
2009-08-01 [J. Antibiot. 62(8) , 465-8, (2009)] |