Elucidation of Piericidin A1 biosynthetic locus revealed a thioesterase-dependent mechanism of α-pyridone ring formation.
Qian Liu, Fen Yao, Yit Heng Chooi, Qianjin Kang, Wei Xu, Yanran Li, Yucheng Shao, Yuefeng Shi, Zixin Deng, Yi Tang, Delin You
文献索引:Chem. Biol. 19(2) , 243-53, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Piericidins are a class of α-pyridone antibiotics that inhibit mitochondrial respiratory chain and exhibit antimicrobial, antifungal, and antitumor activities. Sequential analysis of Streptomyces piomogeues var. Hangzhouwanensis genome revealed six modular polyketide synthases, an amidotransferase, two methyltransferases, and a monooxygenase for piericidin A1 production. Gene functional analysis and deletion results provide overview of the biosynthesis pathway. Furthermore, in vitro characterization of the terminal polyketide synthase module with the thioesterase domain using β-ketoacyl substrates was performed. That revealed a pathway where the α-pyridone ring formation is dependent on hydrolysis of the product β, δ-diketo carboxylic acid by the C-terminal thioesterase followed by amidation and cyclization. These findings set the stage to investigate unusual enzymatic mechanisms in α-pyridone antibiotics biosynthesis, provide a foundation for genome mining of α-pyridone antibiotics, and produce analogs by molecular engineering.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
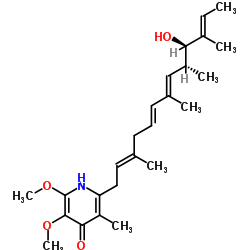 |
粉蝶霉素A
CAS:2738-64-9 |
C25H37NO4 |
|
Isolation and characterizations of quinone analogue-resistan...
1998-09-15 [Biochemistry 37(37) , 12744-52, (1998)] |
|
Etoposide-resistant HT-29 human colon carcinoma cells during...
2008-04-01 [J. Cell Physiol. 215(1) , 243-50, (2008)] |
|
Genetic evidence for the existence of two quinone related in...
1997-03-28 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1319(1) , 1-4, (1997)] |
|
Metabolomic identification of the target of the filopodia pr...
2010-09-24 [Chem. Biol. 17(9) , 989-98, (2010)] |
|
Molecular characterization of benzimidazole resistance in He...
2004-07-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48(7) , 2524-30, (2004)] |