Antioxidant potentials and ajmalicine accumulation in Catharanthus roseus after treatment with giberellic acid.
C Abdul Jaleel, R Gopi, P Manivannan, B Sankar, A Kishorekumar, R Panneerselvam
文献索引:Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 60(2) , 195-200, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Changes in antioxidant potentials and indole alkaloid, ajmalicine, production were studied in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. plants under treatment with gibberellic acid (GA(3)). The GA(3) treatments were given in two ways, foliar spray and soil drenching methods on 30, 45, 60 and 75 days after planting (DAP). The plants were uprooted randomly on 90 DAP and separated into root, stem and leaves and used for analyses. The antioxidant potential was studied in terms of non-enzymatc antioxidant molecules like ascorbic acid (AA), alpha-tocopherol (alpha-toc) and reduced glutathione (GSH) and activities of antioxidant enzyme, viz., superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and catalase (CAT). The alkaloid ajmalicine was extracted and estimated from roots of both control and treated plants. It was found that, GA(3) has a profound effect upon the antioxidant potentials and it caused a significant enhancement in the production of ajmalicine when compared to untreated control as well as foliar-sprayed plants. There was no significant enhancement in GSH and ajmalicine content under GA(3) foliar spray in C. roseus. These preliminary results suggest that, the application of GA(3) may be a useful tool to increase the antioxidant potential and alkaloid production in medicinal plants like C. roseus.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
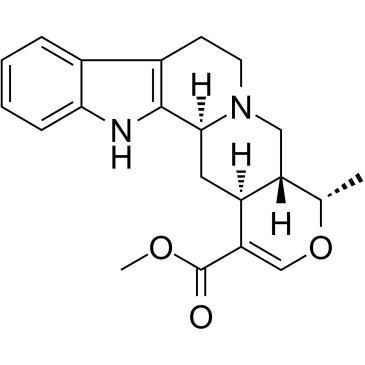 |
萝巴新; 阿吗碱
CAS:483-04-5 |
C21H24N2O3 |
|
Determination of terpenoid indole alkaloids in hairy roots o...
2015-01-01 [Phytochem. Anal. 26 , 331-8, (2015)] |
|
Synergistic and cytotoxic action of indole alkaloids produce...
2013-03-01 [Pharm. Biol. 51(3) , 304-10, (2013)] |
|
A differential response to chemical elicitors in Catharanthu...
2009-04-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 31(4) , 591-5, (2009)] |
|
Molecular modelling of human CYP2D6 and molecular docking of...
2008-05-01 [Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 42(4) , 362-71, (2008)] |
|
Construction and expression of a dual vector for chemo-enzym...
2010-05-01 [Nat. Prod. Res. 24(8) , 759-66, (2010)] |