| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
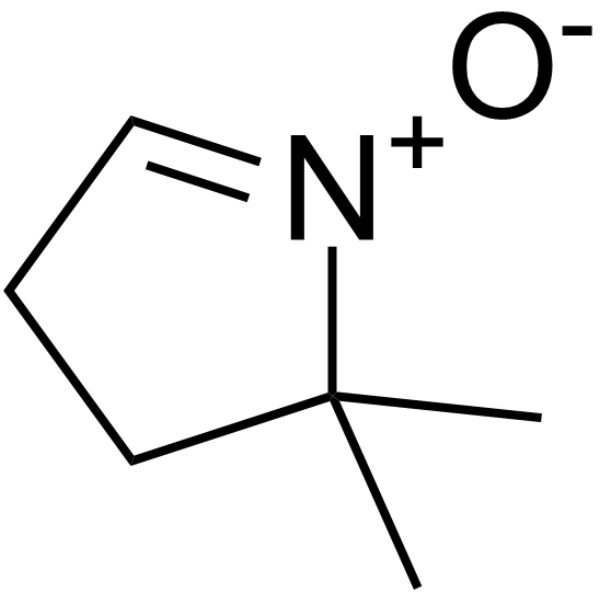 |
5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯啉-N-氧化物
CAS:3317-61-1 |
|
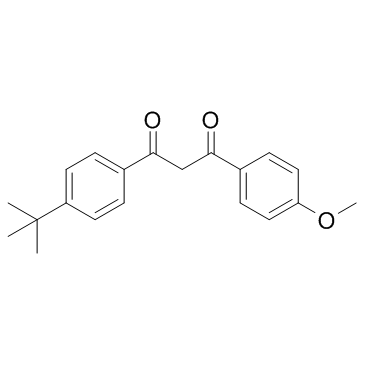 |
阿伏苯宗
CAS:70356-09-1 |