| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-半胱氨酸S-硫酸盐
CAS:1637-71-4 |
|
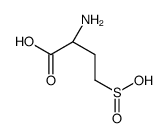 |
D-HOMOCYSTEINESULFINIC ACID
CAS:33514-39-5 |
|
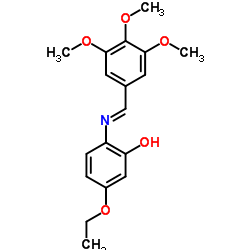 |
L-高半胱氨酸亚磺酸
CAS:2686-70-6 |