Journal of Lipid Research
2011-07-01
A sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS method for rapid diagnosis of Niemann-Pick C1 disease from human plasma.
Xuntian Jiang, Rohini Sidhu, Forbes D Porter, Nicole M Yanjanin, Anneliese O Speak, Danielle Taylor te Vruchte, Frances M Platt, Hideji Fujiwara, David E Scherrer, Jessie Zhang, Dennis J Dietzen, Jean E Schaffer, Daniel S Ory
文献索引:J. Lipid Res. 52(7) , 1435-45, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
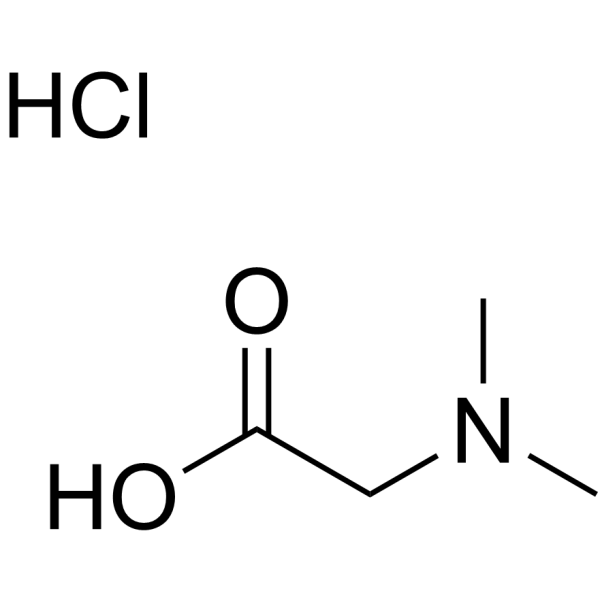
Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) disease is a rare, progressively fatal neurodegenerative disease for which there are no FDA-approved therapies. A major barrier to developing new therapies for this disorder has been the lack of a sensitive and noninvasive diagnostic test. Recently, we demonstrated that two cholesterol oxidation products, specifically cholestane-3β,5α,6β-triol (3β,5α,6β-triol) and 7-ketocholesterol (7-KC), were markedly increased in the plasma of human NPC1 subjects, suggesting a role for these oxysterols in diagnosis of NPC1 disease and evaluation of therapeutics in clinical trials. In the present study, we describe the development of a sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS method for quantifying 3β,5α,6β-triol and 7-KC human plasma after derivatization with N,N-dimethylglycine. We show that dimethylglycine derivatization successfully enhanced the ionization and fragmentation of 3β,5α,6β-triol and 7-KC for mass spectrometric detection of the oxysterol species in human plasma. The oxysterol dimethylglycinates were resolved with high sensitivity and selectivity, and enabled accurate quantification of 3β,5α,6β-triol and 7-KC concentrations in human plasma. The LC-MS/MS assay was able to discriminate with high sensitivity and specificity between control and NPC1 subjects, and offers for the first time a noninvasive, rapid, and highly sensitive method for diagnosis of NPC1 disease.
相关化合物