Interaction of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and methamphetamine during metabolism by in vitro human metabolic enzymes and in rats.
Kenji Kuwayama, Kenji Tsujikawa, Hajime Miyaguchi, Tatsuyuki Kanamori, Yuko T Iwata, Hiroyuki Inoue
文献索引:J. Forensic Sci. 57(4) , 1008-13, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Illicit amphetamine-type stimulant (ATS) tablets commonly contain one or more active ingredients, which have hallucinogenic and/or stimulant effects. Because components such as 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and methamphetamine (MA) in ATS tablets have similar chemical structures, they could be metabolized by common metabolic enzymes. To investigate potential metabolic interactions of ATS tablet components, we studied the in vitro metabolism of MDMA and MA using human metabolic enzymes. MDMA and MA were mainly metabolized by cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) and mutually inhibited the production of their main metabolites. In vivo experiments were also performed using intravenous administration of MDMA, MA, or their mixture to rats. The plasma concentrations of MDMA and MA after co-administration were higher than those after administration of MDMA or MA alone. The results in this study imply that multiple components in ATS tablets can interact to mutually inhibit their metabolism and potentially enhance the toxicity of each component.© 2011 American Academy of Forensic Sciences.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
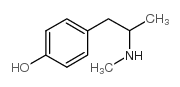 |
甲羟苯丙胺
CAS:370-14-9 |
C10H15NO |
|
Identification of new urinary metabolites of famprofazone in...
1998-01-01 [J. Anal. Toxicol. 22(1) , 55-60, (1998)] |
|
Urinary excretion of the main metabolites of methamphetamine...
2006-01-01 [Xenobiotica 36(2-3) , 259-67, (2006)] |
|
LC-MS/MS analysis of pholedrine in a fatal intoxication case...
2003-04-23 [Forensic Sci. Int. 133(1-2) , 101-6, (2003)] |
|
p-Hydroxymethamphetamine enantiomer pharmacokinetics and met...
1997-07-01 [Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 18(5) , 423-32, (1997)] |
|
[Horner's syndrome secondary to ophthalmic herpes zoster].
1997-12-01 [Rev. Neurol. 25(148) , 1922-4, (1997)] |