Studies on the mechanism of nabam- and zineb-induced inhibition of the hepatic microsomal monooxygenases of the male rat.
C Borin, A Periquet, S Mitjavila
文献索引:Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 81(3 Pt 1) , 460-8, (1985)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In vitro effects of the ethylene bis-dithiocarbamate fungicides, nabam and zineb, on the hepatic microsomal monooxygenases of male rats were examined. Incubation of nabam and zineb with hepatic microsomes, without NADPH, leads to an inhibition of the metabolism of aminopyrine and aniline and to a denaturation of cytochrome P-450 into cytochrome P-420; in addition nabam causes the destruction of cytochrome P-450. Addition of NADPH into the incubation medium increases the inhibition of the monooxygenases, principally the inhibition of the metabolism of aniline induced by nabam. We studied the in vitro effects of three of the chief breakdown products of these fungicides: ethylene bis-isothiocyanate sulfide (EBIS), ethylene thiourea (ETU), and carbon disulfide (CS2). EBIS appears to be the only metabolite affecting directly (without NADPH) the hepatic monooxygenases activity. EBIS accounted partly for nabam-induced inhibition of the hepatic microsomal monooxygenases. The data suggest that the decrease of monooxygenases activity seen on incubation of nabam with hepatic microsomes may be due to the denaturation and destruction of cytochrome P-450 resulting from covalent binding of the compounds with cysteine sulfhydryl groups in cytochrome P-450. Inhibition of monooxygenase activity induced by zineb seems to be due to the reaction with the sulfhydryl groups of cytochrome P-450 and to another mechanism, probably related to its lipophilic character.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
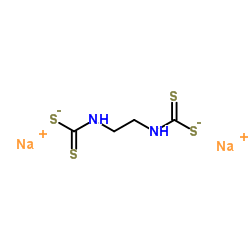 |
代森钠
CAS:142-59-6 |
C4H6N2Na2S4 |
|
[Hepatic microsomal monoxygenase inhibition by nabam in the ...
1981-11-01 [Toxicol. Eur. Res. 3(6) , 285-91, (1981)] |
|
Ultrastructural and histological study of degenerative chang...
1983-05-01 [J. Invertebr. Pathol. 41(3) , 281-300, (1983)] |
|
[Effects of the fungicides, nabam and zineb, on oxygenase ac...
1981-12-01 [Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 19(6) , 761-3, (1981)] |
|
Determination of nabam fungicide in crops by liquid chromato...
1991-01-01 [J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 74(2) , 384-8, (1991)] |
|
Photodegradation and flow-injection determination of dithioc...
2009-03-01 [Anal. Sci. 25(3) , 395-400, (2009)] |