| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
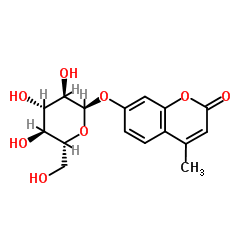 |
4-甲基香豆素基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
CAS:17833-43-1 |
|
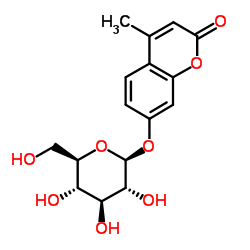 |
4-甲基伞形酮-β-D-葡糖苷
CAS:18997-57-4 |