Expression of Trichoderma reesei β-mannanase in tobacco chloroplasts and its utilization in lignocellulosic woody biomass hydrolysis.
Pankaj Agrawal, Dheeraj Verma, Henry Daniell
文献索引:PLoS ONE 6(12) , e29302, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Lignocellulosic ethanol offers a promising alternative to conventional fossil fuels. One among the major limitations in the lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis is unavailability of efficient and environmentally biomass degrading technologies. Plant-based production of these enzymes on large scale offers a cost-effective solution. Cellulases, hemicellulases including mannanases and other accessory enzymes are required for conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into fermentable sugars. β-mannanase catalyzes endo-hydrolysis of the mannan backbone, a major constituent of woody biomass. In this study, the man1 gene encoding β-mannanase was isolated from Trichoderma reesei and expressed via the chloroplast genome. PCR and Southern hybridization analysis confirmed site-specific transgene integration into the tobacco chloroplast genomes and homoplasmy. Transplastomic plants were fertile and set viable seeds. Germination of seeds in the selection medium showed inheritance of transgenes into the progeny without any Mendelian segregation. Expression of endo-β-mannanase for the first time in plants facilitated its characterization for use in enhanced lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis. Gel diffusion assay for endo-β-mannanase showed the zone of clearance confirming functionality of chloroplast-derived mannanase. Endo-β-mannanase expression levels reached up to 25 units per gram of leaf (fresh weight). Chloroplast-derived mannanase had higher temperature stability (40 °C to 70 °C) and wider pH optima (pH 3.0 to 7.0) than E.coli enzyme extracts. Plant crude extracts showed 6-7 fold higher enzyme activity than E.coli extracts due to the formation of disulfide bonds in chloroplasts, thereby facilitating their direct utilization in enzyme cocktails without any purification. Chloroplast-derived mannanase when added to the enzyme cocktail containing a combination of different plant-derived enzymes yielded 20% more glucose equivalents from pinewood than the cocktail without mannanase. Our results demonstrate that chloroplast-derived mannanase is an important component of enzymatic cocktail for woody biomass hydrolysis and should provide a cost-effective solution for its diverse applications in the biofuel, paper, oil, pharmaceutical, coffee and detergent industries.© 2011 Agrawal et al.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
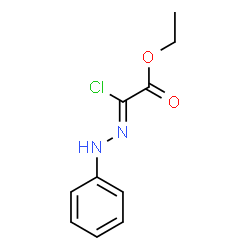 |
槐豆胶
CAS:9000-40-2 |
C10H11ClN2O2 |
|
Determination of D-pinitol in carob syrup.
2011-09-01 [Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 62(6) , 572-6, (2011)] |
|
Purification and characterization of Aspergillus terreus α-g...
2011-08-01 [Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 164(7) , 1111-25, (2011)] |
|
Efficacy of the combined application of chitosan and Locust ...
2014-01-17 [Int. J. Food Microbiol. 170 , 21-8, (2014)] |
|
Influence of a family 29 carbohydrate binding module on the ...
2016-02-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1860 , 354-62, (2015)] |
|
A new approach for the synthesis of hyperbranched N-glycan c...
2013-12-20 [Org. Lett. 15(24) , 6278-81, (2013)] |