Evaluation of the genotoxicity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and its derivatives in mammalian cell cultures.
B B Gollapudi, J M Charles, V A Linscombe, S J Day, J S Bus
文献索引:Mutat. Res. 444(1) , 217-25, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and its derivatives (collectively known as 2,4-D) are herbicides used to control a wide variety of broadleaf and woody plants. The genetic toxicity of an ester (2,4-D 2-butoxyethylester) and two salts (2,4-D isopropylamine and 2,4-D triisopropanolamine) was investigated in cultured mammalian cells. The end points used were the induction of chromosomal aberrations in primary cultures of rat lymphocytes and forward mutations at the HGPRT locus of Chinese hamster ovary cells. There was no evidence of genotoxicity for the test materials in the experimental systems used. These results were consistent with the general lack of genotoxic potential for 2,4-D in a number of other test systems.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
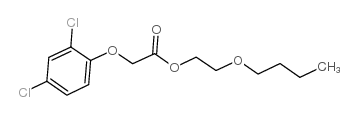 |
2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸丁氧基乙基酯
CAS:1929-73-3 |
C14H18Cl2O4 |
|
Interactions of skin thickness and physicochemical propertie...
2006-05-01 [Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 79(5) , 405-13, (2006)] |
|
In vivo micronucleus assays on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic aci...
1999-07-21 [Mutat. Res. 444(1) , 227-34, (1999)] |
|
Toxicities of butoxyethanol ester and propylene glycol butyl...
1985-03-01 [Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 14(2) , 153-60, (1985)] |
|
Stress response of juvenile sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus ner...
1981-12-01 [Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27(6) , 877-84, (1981)] |
|
Acute toxicity to juvenile Pacific salmonids and rainbow tro...
1990-10-01 [Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 45(4) , 604-11, (1990)] |