Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to butylate in the Agricultural Health Study (AHS)
Shannon M. Lynch, Rajeev Mahajan, Laura E. Beane Freeman, Jane A. Hoppin, Michael C.R. Alavanja, Shannon M. Lynch, Rajeev Mahajan, Laura E. Beane Freeman, Jane A. Hoppin, Michael C.R. Alavanja
文献索引:Environ. Res. 109(7) , 860-8, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Although limited, epidemiologic studies suggest possible associations between butylate use and cancer risk, specifically prostate cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). We examined butylate use and cancer risk more broadly in the AHS, a cohort of licensed pesticide applicators in Iowa and North Carolina. Pesticide use information was collected using self-administered questionnaires. Poisson regression was used to calculate rate ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Two exposure metrics were used: lifetime exposure days (LD) and intensity-weighted lifetime exposure days (IWLD). We used two referent groups: unexposed to butylate and the lowest butylate usage category. This analysis included 19,655 applicators with complete butylate use information; 5297 applicators were exposed to butylate, making this the largest study of butylate to date. The mean follow-up time since enrollment was 9 years. Prostate cancer risk was significantly elevated among applicators in the highest LD category in both referent groups (low-exposed referent: RR LD=2.09, 95% CI=1.27–3.44). We observed a significantly elevated joint effect of prostate cancer family history and high butylate usage across both exposure metrics and both referent groups (low-exposed referent: RR LD=2.00, 95% CI=1.07–3.74), and a non-significant, elevated interaction between butylate use and prostate cancer family history, similar to a previous AHS finding. Statistically significant increased risks and exposure–response trends were seen for all lymphohematopoietic cancers (AL) and NHL for both exposure metrics and referent groups (low-exposed referent: AL:RR LD=2.27, 95% CI=1.18–4.37; NHL: RR LD=3.44, 95% CI=1.29–9.21). Our analysis did not find meaningful associations for other cancers analyzed. Further study is warranted for AL, NHL and prostate cancers.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
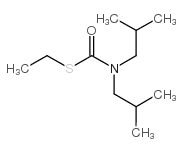 |
丁草敌
CAS:2008-41-5 |
C11H23NOS |
|
Sorption to black carbon of organic compounds with varying p...
2005-05-15 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(10) , 3688-94, (2005)] |
|
Cytogenetic effect of the thiocarbamate herbicides butylate,...
1990-12-01 [Mutat. Res. 242(4) , 279-83, (1990)] |
|
Agricultural exposure to carbamate pesticides and risk of no...
2001-07-01 [J. Occup. Environ. Med. 43(7) , 641-9, (2001)] |
|
Enhanced functional maturation of fetal porcine hepatocytes ...
2006-01-01 [Cell. Transplant. 15(8-9) , 799-809, (2006)] |
|
[Effect of sutan on the soil microflora in corn plantings].
1980-01-01 [Mikrobiol. Zh. 42(1) , 39-43, (1980)] |