Blockade of the glycine modulatory site of NMDA receptors modifies dynorphin-induced behavioral effects.
R Bakshi, A I Faden
文献索引:Neurosci. Lett. 110(1-2) , 113-7, (1990)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Intrathecal (i.t.) administration of the opioid dynorphin causes neurological dysfunction and tissue damage. It has been suggested that these effects of dynorphin may be mediated, in part, by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. In the present studies, recently developed compounds that block the glycine potentiation site of the NMDA receptor (Gly-NMDA site), including the competitive antagonist 5-fluoro-indole-2-carboxylic acid and the non-competitive antagonist 7-chlorokynurenic acid, prevented the neurologic deficits and mortality caused by i.t. dynorphin A(1-17). These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that dynorphin-induced neurological dysfunction involves activation of NMDA receptors. Moreover, blockade of the Gly-NMDA site may provide an alternative to blockade of the glutamate binding site or NMDA receptor ion channel as an in vivo pharmacological strategy to treat conditions previously associated with excitotoxin mediated tissue injury.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
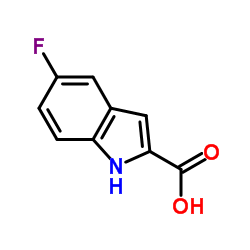 |
5-氟吲哚-2-甲酸
CAS:399-76-8 |
C9H6FNO2 |
|
Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship studie...
2014-12-01 [J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 29(6) , 846-67, (2014)] |
|
Stable benzotriazole esters as mechanism-based inactivators ...
2006-03-01 [Chem. Biol. 13(3) , 261-8, (2006)] |
|
Effect of 5-fluoroindole-2-carboxylic acid (an antagonist of...
1998-01-01 [J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 105(2-3) , 133-46, (1998)] |
|
Quisqualate activates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels...
1990-04-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 37(4) , 477-81, (1990)] |
|
Enhanced sensitivity of medullary depressor neurons to N-met...
2014-07-01 [Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 25(3-4) , 216-9, (1998)] |