Salicylic acid triggers genotoxic adaptation to methyl mercuric chloride and ethyl methane sulfonate, but not to maleic hydrazide in root meristem cells of Allium cepa L.
Jita Patra, Malaya K Sahoo, Brahma B Panda
文献索引:Mutat. Res. 581(1-2) , 173-80, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Salicylic acid (SA), 0.01 mM, a signalling phytohormone, was tested for induction of adaptive response against genotoxicity of methyl mercuric chloride (MMCl), 0.013 mM; ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS), 2.5 mM, or maleic hydrazide (MH), 5 mM, in root meristem cells of Allium cepa. Induction of adaptive response to EMS by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), 1 mM, and yet another secondary signal molecule was tested for comparison. Assessed by the incidence of mitoses with spindle and/or chromosome aberration and micronucleus, the findings provided evidence that SA-conditioning triggered adaptive response against the genotoxic-challenges of MMCl and EMS, but failed to do so against MH. H2O2, which is known to induce adaptive response to MMCl and MH, failed to induce the same against EMS in the present study. The findings pointed to the possible role of signal transduction in the SA-induced adaptive response to genotoxic stress that perhaps ruled out an involvement of H2O2.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
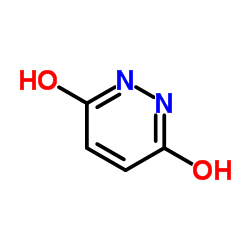 |
马来酰肼
CAS:123-33-1 |
C4H4N2O2 |
|
Mixture genotoxicity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, acry...
2015-01-01 [J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 78(6) , 369-80, (2015)] |
|
Assessment of the chemical, microbiological and toxicologica...
2014-10-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 108 , 294-301, (2014)] |
|
Glyphosate, alachor and maleic hydrazide have genotoxic effe...
2012-05-01 [Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 88(5) , 659-65, (2012)] |
|
The Fate of maleic hydrazide on tobacco during smoking.
2012-01-01 [ScientificWorldJournal 2012 , 451471, (2012)] |
|
Maleic hydrazide residues in tobacco and their toxicological...
1987-01-01 [Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 98 , 43-60, (1987)] |