Metabolic potentiation of the radiosensitization of hypoxic bacterial cells afforded by nitroaromatic compounds.
R F Anderson, K B Patel
文献索引:Radiat. Res. 93(3) , 516-24, (1983)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Prolonged preirradiation incubation of nitroaromatic radiosensitizers with Escherichia coli cells has been found to increase the degree of radiosensitization of the cells in anoxia. Studies with E. coli strains which differ in their nitroreductase activity indicate that the increase in sensitization arises from the action of metabolites produced by the nitroreductase system of the cell. The metabolites alone appear to decrease the extrapolation number of irradiated hypoxic cells and when combined with the parent compound give a biphasic survival curve. The combination of misonidazole (1 mmole dm-3) and its metabolites (1 mmole dm-3) gave initial and final enhancement ratios of 2.4 and 1.4, respectively. The final enhancement ratio is that expected for 1 mmole dm-3 misonidazole alone, whereas the initial enhancement ratio indicates that the metabolites potentiate the action of misonidazole. The preirradiation incubation effect is removed by dithiothreitol at concentrations which do not affect the radiosensitization level of the nitroaromatic sensitizer. This result indicates that the active metabolite probably depletes a certain amount of the free-thiol compounds inside the cell which assist in the repair of radiation-induced damage.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
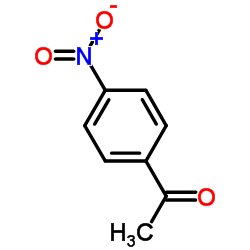 |
对硝基苯乙酮
CAS:100-19-6 |
C8H7NO3 |
|
Analysis of the Photodegradation of the Imidazolinone Herbic...
2015-12-23 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 10768-77, (2015)] |
|
[Semiconservative and unscheduled DNA-synthesis of rat thymo...
1982-02-01 [Strahlentherapie 158(2) , 112-22, (1982)] |
|
Structure-reactivity effects on primary deuterium isotope ef...
2009-10-07 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(39) , 13952-62, (2009)] |
|
Modification of radiation sensitivity of Bacillus megaterium...
1974-06-01 [Radiat. Res. 58(3) , 481-8, (1974)] |
|
The effect of combinations of nitroaromatic and nitroxyl rad...
1981-11-01 [Radiat. Res. 88(2) , 369-76, (1981)] |