| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
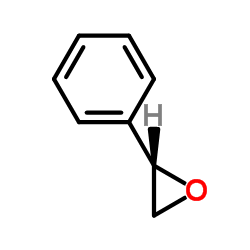 |
(S)-环氧苯乙烷
CAS:20780-54-5 |
|
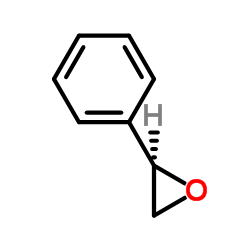 |
(R)-环氧苯乙烷
CAS:20780-53-4 |
|
 |
氧化苯乙烯
CAS:96-09-3 |