The synthetic PPARgamma agonist troglitazone inhibits IL-5-induced CD69 upregulation and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin release from eosinophils.
Yoshinori Matsuwaki, Shigeharu Ueki, Tetsuya Adachi, Hajime Oyamada, Yumiko Kamada, Kazutoshi Yamaguchi, Akira Kanda, Kazuyuki Hamada, Hiroyuki Kayaba, Junichi Chihara
文献索引:Pharmacology 74(4) , 169-73, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) is a nuclear receptor that regulates lipid metabolism. Recently, PPARgamma was reported to be a negative regulator in the immune system. Eosinophils also express PPARgamma, however, the role of PPARgamma in eosinophil functions is not well understood. Surface expression of CD69 and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) release are well-known activation markers of eosinophils. We investigated the effect of a PPARgamma agonist on human eosinophil functions such as IL-5-induced CD69 surface expression and EDN release. IL-5 significantly induced eosinophil CD69 surface expression analyzed using flow cytometry and EDN release measured by ELISA. IL-5-induced eosinophil CD69 surface expression and EDN release were significantly inhibited by the synthetic PPARgamma agonist troglitazone, and these effects were reversed by a PPARgamma antagonist. The PPARgamma agonist troglitazone has a potent inhibitory effect on activation and degranulation of eosinophils, and it may be a therapeutic modality for the treatment of allergic diseases.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
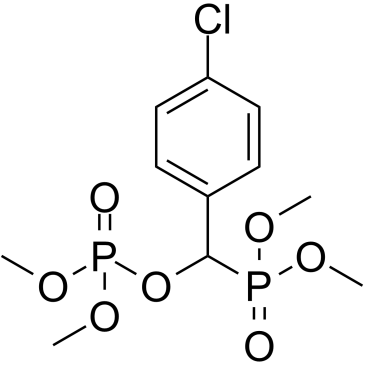 |
米福贝特
CAS:76541-72-5 |
C11H17ClO7P2 |
|
Inhibitory effect of baicalin on iNOS and NO expression in i...
2013-01-01 [PLoS ONE 8 , e80997, (2013)] |
|
Do peroxisome proliferation receptor-gamma antagonists have ...
2003-04-01 [Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 12(4) , 713-6, (2003)] |
|
Antitumorigenic effect of Wnt 7a and Fzd 9 in non-small cell...
2006-09-15 [J. Biol. Chem. 281(37) , 26943-50, (2006)] |
|
Interference of dimethyl alpha-(dimethoxyphosphinyl) p-chlor...
1987-01-01 [J. Endocrinol. 112(1) , 171-5, (1987)] |
|
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma contributes...
2006-01-01 [J. Leukoc. Biol. 79(1) , 235-43, (2006)] |