Dietary supplementation with 3-deaza adenosine, N-acetyl cysteine, and S-adenosyl methionine provide neuroprotection against multiple consequences of vitamin deficiency and oxidative challenge: relevance to age-related neurodegeneration.
Flaubert Tchantchou, Michael Graves, Daniela Ortiz, Eugene Rogers, Thomas B Shea
文献索引:Neuromolecular Med. 6(2-3) , 93-103, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Folate deprivation induces neurotoxicity that is potentiated by additional nutritional and genetic deficiencies including vitamin E and apolipoprotein E deficiency. These deficiencies collectively induce oxidative damage, cognitive impairment, and compensatory alteration in glutathione generation. Treatment with agents that regulate distinct portions of the methionine cycle, including the S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase inhibitor, 3-deaza adenosine, the methyl donor S-adenosyl methionine, and the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine, provide neuroprotection against various aspects of neurotoxicity in normal and apolipoprotein E-deficient mice and in cultured neuronal cells deprived of dietary folate and vitamin E and subjected to iron overload. Here it is demonstrated that simultaneous treatment with these agents provide superior neuroprotection by alleviating individual and overlapping neurotoxic consequences. These findings support combinatorial treatments with agents that compensate for differential insults in age-related neurodegenerative disorders.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
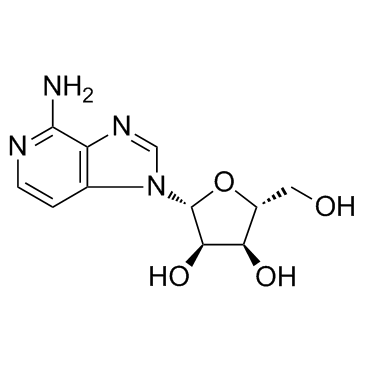 |
3-Deaza-腺苷
CAS:6736-58-9 |
C11H14N4O4 |
|
Disruption of choline methyl group donation for phosphatidyl...
2002-05-10 [J. Biol. Chem. 277(19) , 17217-25, (2002)] |
|
Activation of caspase-8 in 3-deazaadenosine-induced apoptosi...
2001-12-31 [Exp. Mol. Med. 33(4) , 284-92, (2001)] |
|
Identification of A-minor tertiary interactions within a bac...
2002-08-20 [Biochemistry 41(33) , 10426-38, (2002)] |
|
3-Deazaadenosine inhibits vasa vasorum neovascularization in...
2009-01-01 [Atherosclerosis 202(1) , 103-10, (2009)] |
|
Protein methylation activates reconstituted ryanodine recept...
2004-01-01 [J. Vasc. Res. 41(3) , 229-40, (2004)] |