Crucial role of SLP-76 and ADAP for neutrophil recruitment in mouse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Helena Block, Jan M Herter, Jan Rossaint, Anika Stadtmann, Stefanie Kliche, Clifford A Lowell, Alexander Zarbock
文献索引:J. Exp. Med. 209 , 407-21, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Neutrophils trigger inflammation-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), a frequent and potentially lethal occurrence in humans. Molecular mechanisms underlying neutrophil recruitment to sites of inflammation have proved elusive. In this study, we demonstrate that SLP-76 (SH2 domain-containing leukocyte phosphoprotein of 76 kD) and ADAP (adhesion and degranulation promoting adaptor protein) are involved in E-selectin-mediated integrin activation and slow leukocyte rolling, which promotes ischemia-reperfusion-induced AKI in mice. By using genetically engineered mice and transduced Slp76(-/-) primary leukocytes, we demonstrate that ADAP as well as two N-terminal-located tyrosines and the SH2 domain of SLP-76 are required for downstream signaling and slow leukocyte rolling. The Tec family kinase Bruton tyrosine kinase is downstream of SLP-76 and, together with ADAP, regulates PI3Kγ (phosphoinositide 3-kinase-γ)- and PLCγ2 (phospholipase Cγ2)-dependent pathways. Blocking both pathways completely abolishes integrin affinity and avidity regulation. Thus, SLP-76 and ADAP are involved in E-selectin-mediated integrin activation and neutrophil recruitment to inflamed kidneys, which may underlie the development of life-threatening ischemia-reperfusion-induced AKI in humans.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
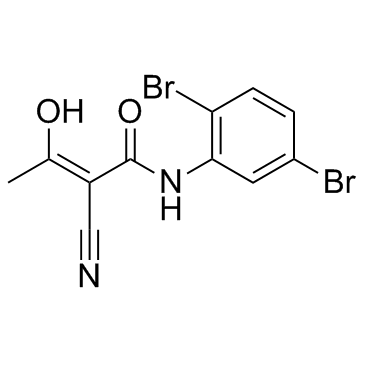 |
(2Z)-2-氰基-N-(2,5-二溴苯基)-3-羟基-2-丁烯酰胺
CAS:244240-24-2 |
C11H8Br2N2O2 |
|
Phagocytosis-dependent activation of a TLR9-BTK-calcineurin-...
2015-03-01 [EMBO Mol. Med. 7(3) , 240-58, (2015)] |
|
Epigenetic regulation of CpG promoter methylation in invasiv...
2010-01-01 [Mol. Cancer 9 , 267, (2010)] |
|
Alternatively activated macrophage-derived RELM-{alpha} is a...
2009-04-13 [J. Exp. Med. 206(4) , 937-52, (2009)] |
|
'Clustering' SIRPα into the plasma membrane lipid microdomai...
2013-01-01 [PLoS ONE 8 , e77615, (2013)] |
|
Different roles for non-receptor tyrosine kinases in arachid...
2006-01-01 [J. Inflamm. (Lond.) 3 , 8, (2006)] |