Isolation and characterization of fenamiphos degrading bacteria.
J Alfonso Cabrera, Andreas Kurtz, Richard A Sikora, Alexander Schouten
文献索引:Biodegradation 21(6) , 1017-27, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The biological factors responsible for the microbial breakdown of the organophosphorus nematicide fenamiphos were investigated. Microorganisms responsible for the enhanced degradation of fenamiphos were isolated from soil that had a long application history of this nematicide. Bacteria proved to be the most important group of microbes responsible for the fenamiphos biodegradation process. Seventeen bacterial isolates utilized the pure active ingredient fenamiphos as a carbon source. Sixteen isolates rapidly degraded the active ingredient in Nemacur 5GR. Most of the fenamiphos degrading bacteria were Microbacterium species, although Sinorhizobium, Brevundimonas, Ralstonia and Cupriavidus were also identified. This array of gram positive and gram negative fenamiphos degrading bacteria appeared to be pesticide-specific, since cross-degradation toward fosthiazate, another organophosphorus pesticide used for nematode control, did not occur. It was established that the phylogenetical relationship among nematicide degrading bacteria is closer than that to non-degrading isolates.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
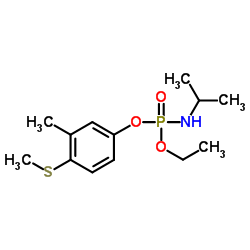 |
苯线磷
CAS:22224-92-6 |
C13H22NO3PS |
|
Factors affecting the efficacy of non-fumigant nematicides f...
2005-10-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 61(10) , 961-72, (2005)] |
|
Enhanced microbial degradation of cadusafos in soils from po...
2004-08-01 [Chemosphere 56(6) , 549-59, (2004)] |
|
Detections of eleven organophosphorus insecticides and one h...
2011-10-01 [Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 87(4) , 355-60, (2011)] |
|
Influence of pore water velocity on the release of carbofura...
2012-11-01 [J. Contam. Hydrol. 142-143 , 75-81, (2012)] |
|
Zinc(II) phthalocyanines immobilized in mesoporous silica Al...
2012-09-30 [J. Hazard. Mater. 233-234 , 79-88, (2012)] |