Quinones facilitate the self-assembly of the phosphorylated tubulin binding region of tau into fibrillar polymers.
Ismael Santa-María, Félix Hernández, Concepción Pérez Martín, Jesús Avila, Francisco J Moreno
文献索引:Biochemistry 43(10) , 2888-97, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The fragment of tau containing the first and third tubulin-binding motifs, involved in self-assembly of tau, was phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA). In the presence of hydroxynonenal (HNE) or in the presence of quinones such as juglone, 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone (coenzyme Q(0) or DMM), or menadione, the polymerization of this phosphorylated tau fragment is catalyzed, whereas polymerization of the unmodified fragment takes place in a lesser extent. The quinones coenzyme Q(0) and menadione are found in every cell, including neural cells, and may interact with tau protein to facilitate its assembly into filamentous structures. These tau filaments, assembled in the presence of quinones, have a fibrillar morphology very similar to that of paired helical filaments present in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
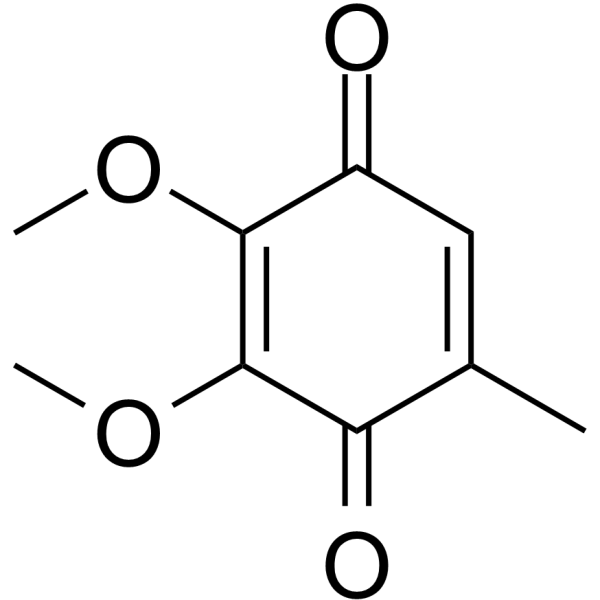 |
2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基-1,4-苯醌
CAS:605-94-7 |
C9H10O4 |
|
Cofactor Specificity of the Bifunctional Alcohol and Aldehyd...
2015-08-01 [J. Bacteriol. 197 , 2610-9, (2015)] |
|
Prerequisites for ubiquinone analogs to prevent mitochondria...
2012-02-01 [J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 44(1) , 207-12, (2012)] |
|
Ubiquinone analogs: a mitochondrial permeability transition ...
2010-01-01 [PLoS ONE 5 , e11792, (2010)] |
|
Immunochemical identification of coenzyme Q0-dihydrolipoamid...
2004-06-25 [J. Biol. Chem. 279 , 27278-27285, (2004)] |
|
Photolabile ubiquinone analogues for identification and char...
2010-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 3457-66, (2010)] |