Absorption of Intralipid and interferences from nutrients infused into the peritoneal cavity of the rat.
G Mahedero, J M Morán, J Salas, M Blanco
文献索引:Am. J. Surg. 164 , 45-50, (1992)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We studied the peritoneal absorption and elimination of Intralipid after its intraperitoneal and intravenous infusion into rats, by means of a two-compartment model. Follow-up measurements of the plasma triglyceride rate were made. The peritoneal absorption of Intralipid gives the following absorption and elimination constants: Ka (absorption constant from the peritoneal cavity) is 0.106 +/- 0.08 h-1; Ke (elimination constant from the blood stream) is 0.0440 +/- 08 h-1; and BAa (absolute bioavailability) is 84.5 +/- 0.08% 8 hours after infusion. These results show that the intraperitoneal absorption of Intralipid is high and progressive during the first 8 hours, thus supplying the daily caloric needs of the animal through the administration of a single bolus administration, and the plasma triglyceride clearance is faster than the intraperitoneal absorption after the first 6 hours, thus avoiding dangerous overloads. We also studied the behavior of different combinations of glucose, amino acids, and fats infused into the peritoneal cavity of rats in order to observe possible interferences with the absorption of these nutrients. Two microcuries of radioactive L-glucose-1-C14 with 5 mL of 5% D-glucose, with 5 mL of 3.5% amino-acid solution, or with 5 mL of 20% fat emulsion were infused intraperitoneally into three different groups of animals. Slight differences of plasma radioactivity were registered among these three groups 1 hour after infusion. Likewise, small differences of plasma radioactivity were observed between the animals receiving an infusion of 1 microCi of five L-amino-acids-U-C14 diluted with 5 mL of 3.5% amino-acid solution, with 5 mL of 5% glucose solution, or with 5 mL of 20% fat emulsion 4 and 6 hours after infusion. No differences in the plasma triglyceride rates were observed between those groups of animals infused with 5 mL of 20% Intralipid plus 5 mL of glucose solution or with 20% Intralipid plus 3.5% amino-acid solution compared with the group receiving only 5 mL of 20% Intralipid. The infusion of fats does not seem to interfere with that of other substrates, possibly because of the different absorption route (lymphatic for fats and capillary vessels for amino acids and glucose solutions), but further research is needed to reach conclusive results. Perhaps the prolonged administration of fat, together with other substrates, produces precipitates and other galenic problems that hinder absorptive mechanisms of the preparations.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
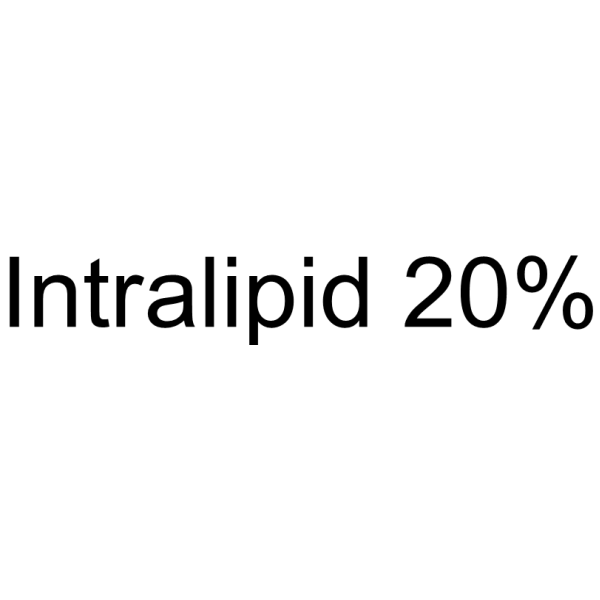 |
脂肪乳剂
CAS:68890-65-3 |
C60H115NO10P |
|
Glucagon receptor antagonism induces increased cholesterol a...
2015-11-01 [J. Lipid Res. 56 , 2183-95, (2015)] |
|
Effect of aging on anticonflict and CNS depressant activity ...
1987-01-01 [Psychopharmacology 93 , 443, (1987)] |
|
Counter-regulatory response to a fall in circulating fatty a...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9 , e113291, (2014)] |
|
Analysis of skin lesions using laminar optical tomography.
2012-07-01 [Biomed. Opt. Express 3 , 1701-12, (2012)] |
|
In vivo microscopy of hemozoin: towards a needle free diagno...
2015-09-01 [Biomed. Opt. Express 6 , 3462-74, (2015)] |