Cytolysis of human erythrocytes by a covalent antibody-selenium immunoconjugate.
L Chen, J E Spallholz
文献索引:Free Radic. Biol. Med. 19(6) , 713-24, (1995)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A selenium (Se)-containing immunoconjugate of a human anti-erythrocyte membrane antibody (Ab-Se) has been synthesized via oxidation of the carbohydrate moieties of the antibody and covalent coupling with selenocystamine. The isolated Ab-Se immunoconjugate is shown to be more hemolytic than is selenocystamine when expressed on equivalent selenium basis. Native antibody preincubated with the human erythrocytes prevented hemolysis induced by the Ab-Se immunoconjugate. As observed microscopically, the Ab-Se immunoconjugate caused extensive damage to the erythrocyte membrane and lysis. The cytotoxicity of Se toward the human erythrocytes is believed to be caused initially by the localized generation of superoxide (O2.-) within the cell membrane. This is the first demonstration of site-directed immunoselectivity of Se cytotoxicity and demonstrates the potential for a free radical pharmacology based on localized Se-generated O2.-.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
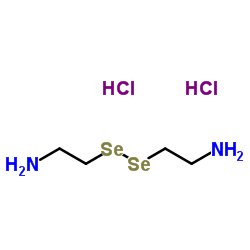 |
硒代胱胺盐酸盐
CAS:3542-13-0 |
C4H14Cl2N2Se2 |
|
Pulse radiolysis studies on reactions of hydroxyl radicals w...
2008-04-10 [J. Phys. Chem. B 112(14) , 4441-6, (2008)] |
|
Oxidation of glutathione and superoxide generation by inorga...
2008-09-01 [Biofactors 31(1) , 55-66, (2007)] |
|
Separation of organoselenium compounds and their electrochem...
2004-07-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 379(5-6) , 770-6, (2004)] |
|
Selenium functionalized intraocular lenses inhibit posterior...
2009-11-01 [Exp. Eye Res. 89(5) , 728-34, (2009)] |
|
Studies on the reducing systems for plant and animal thiored...
2007-09-28 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 361(3) , 629-33, (2007)] |