Measurement of upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model using a positron emitting radiopharmaceutical.
J Zhang, A H Cross, T J McCarthy, M J Welch
文献索引:Nitric Oxide 1(3) , 263-7, (1997)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Excess nitric oxide has been implicated in the pathogenosis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) which is an animal model for multiple sclerosis. Positron emission tomography (PET) is an imaging technique that has shown utility for studying enzyme systems in vivo. A positron-labeled inducible nitric oxide synthetase (iNOS) inhibitor has been studied in EAE-affected mice as well as controls. Greater uptake of the radiolabeled inhibitor was observed in the spinal cord of the affected mice than of control mice. Increased uptake was also observed in other organs not previously implicated in this experimental model. The increased uptake of the radiopharmaceutical in this model suggests that this tracer may have the potential for measuring increased levels of iNOS in humans by PET.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
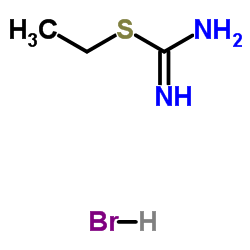 |
S-乙基异硫脲氢溴酸盐
CAS:1071-37-0 |
C3H9BrN2S |
|
Differential activity of NO synthase inhibitors as chemoprev...
2002-01-01 [Neoplasia 4(4) , 332-6, (2002)] |
|
Inotropic response to endothelin-1, isoprenaline and calcium...
2000-07-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 130(6) , 1275-82, (2000)] |
|
Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition attenuates renal ...
2002-02-01 [Hypertension 39(2 Pt 2) , 586-90, (2002)] |
|
Possible role of nitric oxide in anxiety following transient...
2003-01-01 [J. Pharmacol. Sci. 91(1) , 47-52, (2003)] |
|
Nitroarginine and tetrahydrobiopterin binding to the haem do...
1998-05-15 [Biochem. J. 332 ( Pt 1) , 195-201, (1998)] |