| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
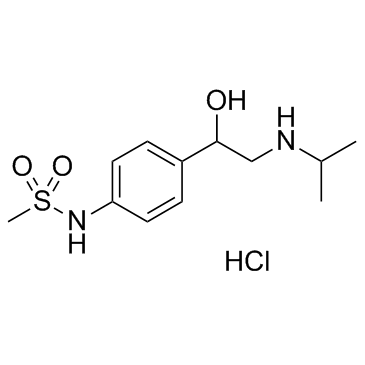 |
盐酸索他洛尔
CAS:959-24-0 |
|
 |
心律平
CAS:34183-22-7 |
|
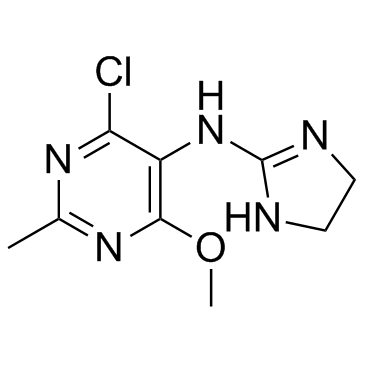 |
莫索尼定
CAS:75438-57-2 |