| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
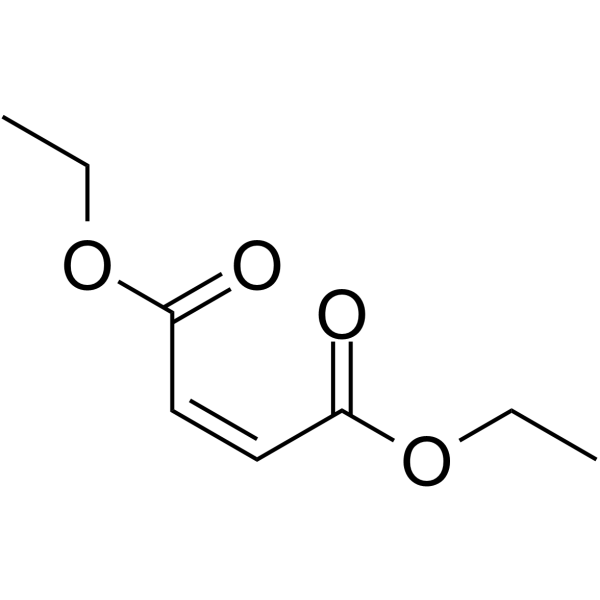 |
顺丁烯二甲酸二乙酯
CAS:141-05-9 |
|
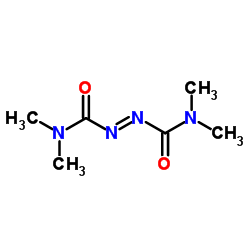 |
偶氮二甲酰胺
CAS:10465-78-8 |
|
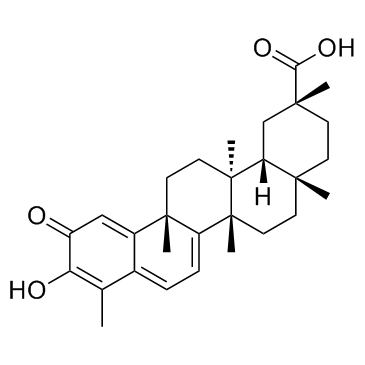 |
雷公藤红素; 南蛇藤素
CAS:34157-83-0 |