Lipid fingerprinting of gram-positive lactobacilli by intact--matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using a proton sponge based matrix.
Cosima D Calvano, Carlo G Zambonin, Francesco Palmisano
文献索引:Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 25 , 1757-1764, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A method of direct lipid analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry (MS) in intact membranes, without prior extraction/separation steps, is described. Here, we demonstrate the efficacy of a strong base, 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene (DMAN; proton sponge), as a novel matrix for MALDI-time-of-flight (TOF) MS analysis of whole cell bacteria. Initially, individual acidic low-molecular-weight analytes such as standard free fatty acids and phospholipids were analyzed using DMAN as matrix. Clear negative-mode MALDI-TOF MS spectra of all analytes show only deprotonated analyte signals at a low picomole limit of detection with the complete absence of matrix-related signals. These results indicate that DMAN represents a suitable matrix for MALDI-TOF MS analysis of mixtures of complex lipids as the intact membranes of microorganisms. DMAN was successfully applied to the analysis of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis and L. plantarum microorganisms. Different components were sensitively detected in a single spot, including 16:0, 18:2, 18:3, and 21:0 free acids, glycolipids, phosphatidylglycerols (PGs) and cardiolipins. This method might be of general application, offering the advantage of quickly gaining information about lipid components of other gram-positive bacterial membranes.Copyright © 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
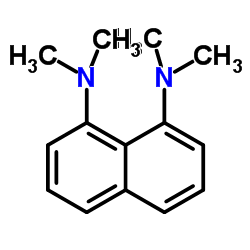 |
1,8-双二甲氨基萘
CAS:20734-58-1 |
C14H18N2 |
|
In situ characterizing membrane lipid phenotype of breast ca...
2015-01-01 [Sci. Rep. 5 , 11298, (2015)] |
|
Distribution study of atorvastatin and its metabolites in ra...
2014-07-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(19) , 4601-10, (2014)] |
|
Proton sponge: a novel and versatile MALDI matrix for the an...
2009-10-01 [Anal. Chem. 81 , 7954-7959, (2009)] |
|
1,8-Bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene: a novel superbasic matrix...
2009-08-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 23 , 2380-2382, (2009)] |
|
Synthesis of C-substituted t-BuNH-8,9-R,R'-nido-7,8,9-C3B8H9...
2010-05-07 [Dalton Trans. 39(17) , 4186-90, (2010)] |