| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
16-DOXYL-硬脂酸 自由基
CAS:53034-38-1 |
|
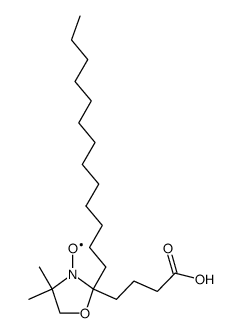 |
5-氮氧自由基硬脂酸
CAS:29545-48-0 |