Effect of hyperthermia and ionizing radiation on the erythrocyte membrane.
E Grzelińska, G Bartosz, W Leyko, I V Chapman
文献索引:Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 42(1) , 45-55, (1982)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Spin-label studies of the effects of hyperthermia on the erythrocyte membrane revealed a decrease in the fluidity of lipids and changes in the state of membrane proteins. The rate of haemolysis in iso-osmotic glycerol solution was increased. Changes of most of the parameters studied when plotted in Arrhenius coordinates revealed a discontinuity (critical hyperthermic transition in the membrane) between 46 and 50 degrees C. Studies of the combined action of ionizing radiation (100 Gy) and hyperthermia (43 degrees C) showed the same direction of changes for (Na-K-Mg)-ATPase activity and spectra of membrane-bound maleimide spin label for both agents, but the additivity of changes depended on the parameter studied.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
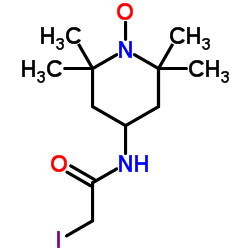 |
4-(2-碘代乙酰氨基)-2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-氧基自由基
CAS:25713-24-0 |
C11H20IN2O2 |
|
A paramagnetic molecular voltmeter.
2008-01-01 [J. Magn. Reson. 190(1) , 7-25, (2008)] |
|
Electron-electron spin-spin interaction in spin-labeled low-...
1995-06-01 [Biophys. J. 68(6) , 2531-42, (1995)] |
|
Phosphorylation regulates the ADP-induced rotation of the li...
1999-08-03 [Biochemistry 38(31) , 10107-18, (1999)] |
|
An iodoacetamide spin-label selectively labels a cysteine si...
1993-10-12 [Biochemistry 32(40) , 10803-11, (1993)] |
|
Resolved conformational states of spin-labeled Ca-ATPase dur...
1992-08-18 [Biochemistry 31(32) , 7381-9, (1992)] |