| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
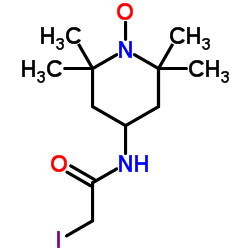 |
4-(2-碘代乙酰氨基)-2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-氧基自由基
CAS:25713-24-0 |
|
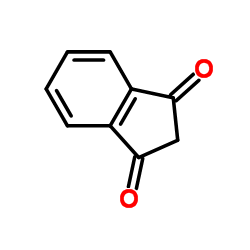 |
1,3-茚满二酮
CAS:606-23-5 |