| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
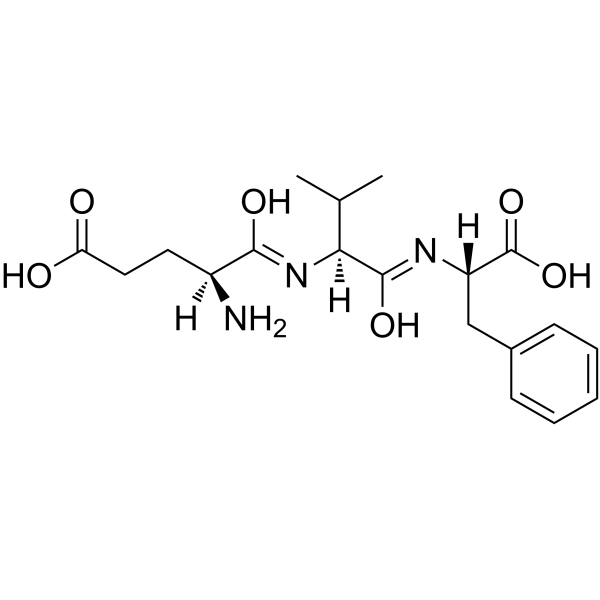 |
L-ALPHA-谷氨酰-L-缬氨酰-L-苯丙氨酸
CAS:31461-61-7 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-ALPHA-谷氨酰-L-缬氨酰-L-苯丙氨酸
CAS:31461-61-7 |