| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
L-1,4-二硫代苏糖醇
CAS:16096-97-2 |
|
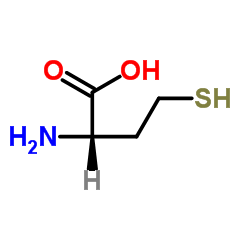 |
L-高半胱氨酸
CAS:6027-13-0 |
|
 |
重酒石酸胆碱
CAS:87-67-2 |