Acetylcholinesterase inhibition promotes retinal vasoprotection and increases ocular blood flow in experimental glaucoma.
Mohammadali Almasieh, Jessica N MacIntyre, Mylène Pouliot, Christian Casanova, Elvire Vaucher, Melanie E M Kelly, Adriana Di Polo
文献索引:Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54(5) , 3171-83, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A clear correlation between vascular deficits and retinal ganglion cell (RGC) loss in glaucoma has not yet been established. The question arose as to whether there is loss of inner retinal vessels following intraocular pressure (IOP) increase and, if so, whether it occurs prior to, concomitantly with, or after RGC death. We also sought to establish whether galantamine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that promotes RGC survival, can protect the retinal microvasculature and enhance blood flow in experimental glaucoma.Ocular hypertension was induced in Brown Norway rats by injection of hypertonic saline into an episcleral vein. Retinas were processed for simultaneous visualization of the retinal microvasculature and RGCs in glaucomatous and control eyes. Retinal blood flow was examined by quantitative autoradiography using N-isopropyl-p-[(14)C]-iodoamphetamine. Vascular reactivity was further assessed using an in vitro retinal microvasculature preparation.Substantial loss of retinal capillaries was observed after induction of ocular hypertension. The onset of both microvasculature and RGC loss occurred early and proceeded at a similar rate for at least 5 weeks after the initial damage. Systemic administration of galantamine preserved microvasculature density and improved retinal blood flow in glaucomatous retinas. The vasoactive effects of galantamine on retinal microvessels occurred through activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors both in vitro and in vivo.The onset and progression of microvessel and RGC loss are concomitant in experimental glaucoma, suggesting a tight codependence between these cellular compartments. Early interventions aimed to protect the retinal microvasculature and improve blood supply are likely to be beneficial for the treatment of glaucoma.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
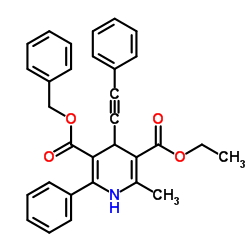 |
乙酰胆碱酯酶 来源于苍蝇头部
CAS:9000-81-1 |
C31H27NO4 | |
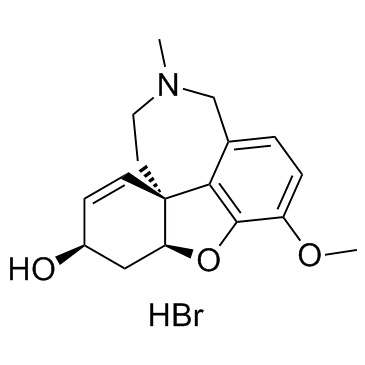 |
氢溴酸加兰他敏
CAS:1953-04-4 |
C17H22BrNO3 |
|
Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-leng...
2004-01-01 [Nat. Genet. 36 , 40-5, (2004)] |
|
The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cD...
2004-10-01 [Genome Res. 14 , 2121-7, (2004)] |
|
Elevated temperatures increase the toxicity of pesticide mix...
2014-01-01 [Aquat. Toxicol. 146 , 38-44, (2014)] |
|
Cerebroprotective effect of isolated harmine alkaloids extra...
2013-12-01 [Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 16(23) , 1687-97, (2013)] |
|
Comparative safety of the antifouling compound butenolide an...
2014-04-01 [Aquat. Toxicol. 149 , 116-25, (2014)] |