Endomembrane H-Ras controls vascular endothelial growth factor-induced nitric-oxide synthase-mediated endothelial cell migration.
Dagmar J Haeussler, David R Pimentel, Xiuyun Hou, Joseph R Burgoyne, Richard A Cohen, Markus M Bachschmid
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 288 , 15380-9, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We demonstrate for the first time that endomembrane-delimited H-Ras mediates VEGF-induced activation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) and migratory response of human endothelial cells. Using thiol labeling strategies and immunofluorescent cell staining, we found that only 31% of total H-Ras is S-palmitoylated, tethering the small GTPase to the plasma membrane but leaving the function of the large majority of endomembrane-localized H-Ras unexplained. Knockdown of H-Ras blocked VEGF-induced PI3K-dependent Akt (Ser-473) and eNOS (Ser-1177) phosphorylation and nitric oxide-dependent cell migration, demonstrating the essential role of H-Ras. Activation of endogenous H-Ras led to recruitment and phosphorylation of eNOS at endomembranes. The loss of migratory response in cells lacking endogenous H-Ras was fully restored by modest overexpression of an endomembrane-delimited H-Ras palmitoylation mutant. These studies define a newly recognized role for endomembrane-localized H-Ras in mediating nitric oxide-dependent proangiogenic signaling.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
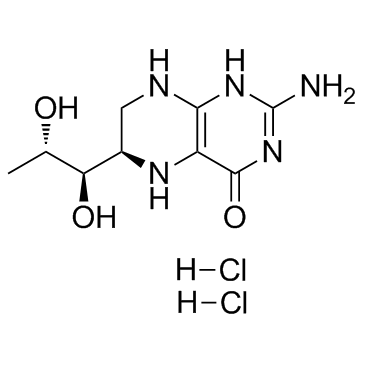 |
(6R)-5,6,7,8-四氢生物蝶呤二盐酸盐
CAS:69056-38-8 |
C9H17Cl2N5O3 |
|
Tetrahydrobiopterin and cytokines.
1993-05-01 [Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 203 , 1, (1993)] |
|
Intravenous treatment of experimental Parkinson's disease in...
2010-09-17 [Brain Res. 1352 , 208-13, (2010)] |
|
A new resorufin-based alpha-glucosidase assay for high-throu...
2009-07-01 [Anal. Biochem. 390 , 79-84, (2009)] |
|
Caveolin-1-eNOS signaling promotes p190RhoGAP-A nitration an...
2011-05-30 [J. Cell Biol. 193 , 841-50, (2011)] |
|
Differential Effects of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro...
2013-02-01 [Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 17 , 89-97, (2013)] |