Effectiveness of cross polarized light and fluorescence diagnosis for detection of sub-clinical and clinical actinic keratosis during imiquimod treatment.
Jean-Paul Ortonne, Girish Gupta, Nicolas Ortonne, Luc Duteil, Catherine Queille, Pascal Mallefet
文献索引:Exp. Dermatol. 19(7) , 641-7, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
During treatment of actinic keratosis (AK) lesions with imiquimod sub-clinical lesions often become visible. It is, however, unclear whether these sub-clinical lesions would be detectable beforehand.The aim of this pilot study was to compare two techniques, cross polarized light photography (CPL) and fluorescence diagnosis (FD) using methyllevulinic acid and illumination with Wood's lamp for their ability to detect sub-clinical lesions. These findings were also compared with biopsy results taken before and after treatment with imiquimod 5% cream or vehicle.Twelve patients with at least five clinically visible AK lesions in a single contiguous 20 cm(2) area on the head were recruited. Patient eligibility was determined at the screening visit, when they were randomized to treatment. The randomization was 3:1, active to vehicle (nine treated with imiquimod, three with vehicle cream) for a total duration of 24 weeks (six clinic visits). Patients were assessed for baseline AK lesion counts (clinical and sub-clinical) at the screening visit and final counts at week 20.The number of clinically observed AK lesions was significantly lower at week 12 and week 20 compared with baseline following imiquimod treatment versus vehicle. The number of counted lesions were significantly higher using the CPL method compared with clinical counting with imiquimod treatment at baseline (8.3 +/- 3.4 vs 5.8 +/- 1.3; P = 0.027) and week 20 (4.8 +/- 2.4 vs 3.0 +/- 1.7; P = 0.02) but not in the vehicle group. The FD lesion counting method did not show a significant increase in the number of detected lesions compared with clinical analysis in the imiquimod and placebo groups but when comparisons were performed using pooled data (treatments and visits combined) the results were significant.The number of sub-clinical and clinical AK lesions detected during treatment with imiquimod can be better demonstrated using the methods of CPL and FD, but statistical significance was reached only using the CPL method. This is only a preliminary study with a small number of patients and as a result it is difficult to conclude both statistical and clinical significance. However, results were encouraging and indicate that larger studies are needed to demonstrate the relevance of these two new methods for improved detection of clinical and especially sub-clinical AK lesions.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
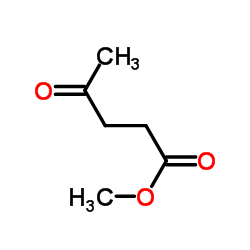 |
乙酰丙酸甲酯
CAS:624-45-3 |
C6H10O3 |
|
Catch-and-release probes applied to semi-intact cells reveal...
2013-02-11 [ChemBioChem. 14(3) , 343-52, (2013)] |
|
One-pot preparation of methyl levulinate from catalytic alco...
2012-09-01 [Carbohydr. Res. 358 , 37-9, (2012)] |
|
First enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-(R)-Pinnatolid...
2012-08-17 [Org. Lett. 14(16) , 4035-7, (2012)] |
|
Interference by methyl levulinate in determination of total ...
1999-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 82(3) , 766-9, (1999)] |
|
Methyl-ALA-induced fluorescence in photodynamic diagnosis of...
2008-01-01 [Arch. Dermatol. 144(1) , 115-7, (2008)] |