Echinacea alkylamides modulate induced immune responses in T-cells.
Anita Matthias, Linda Banbury, Kerry M Bone, David N Leach, Reg P Lehmann
文献索引:Fitoterapia 79(1) , 53-8, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effects of Echinacea and several of its phytochemical components on NFkappaB expression by Jurkat cells (a human T-cell line) were investigated in vitro. In the absence of stimulation, Echinacea and its components exerted no significant effect on basal NFkappaB expression levels. In the presence of endotoxin (LPS), NFkappaB expression was decreased. However, this decrease was significantly reversed by treatment with cichoric acid, an Echinacea root extract (prepared from both Echinacea angustifolia and Echinacea purpurea) and the alkylamide fraction derived from this combination. For the phorbol myristate acetate stimulation of Jurkat cells, effects on NFkappaB expression were mixed. Depending on the concentration, cichoric acid and a 2,4-diene alkylamide significantly induced NFkappaB levels, whereas a 2-ene alkylamide caused a significant inhibition. In contrast, both the Echinacea and the mixed alkylamide fraction exerted no effect. The alkylamide results indicate that the two basic forms of these compounds present in Echinacea may have opposing effects. These opposing effects demonstrate the importance of a knowledge, not only of the phytochemical make-up of a herbal preparation, but also of the actions of each component and the consequences of differing relative amounts in the preparation being investigated.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
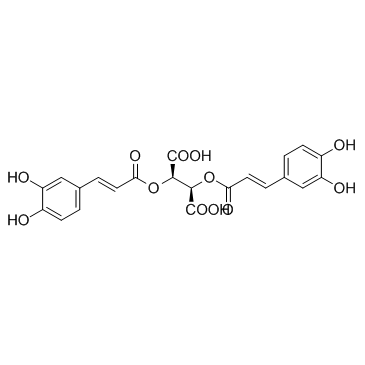 |
菊苣酸
CAS:70831-56-0 |
C22H18O12 |
|
[Simultaneous determination of five organic acids in Kudiezi...
2013-10-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(19) , 3287-90, (2013)] |
|
Application of an online post-column derivatization HPLC-DPP...
2013-02-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 65(2) , 271-9, (2013)] |
|
Large-scale cultivation of adventitious roots of Echinacea p...
2007-08-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 29(8) , 1179-82, (2007)] |
|
Augmentation of immune response by chicoric acid through the...
2011-05-01 [Neuropharmacology 60(6) , 852-60, (2011)] |
|
A cross-over inhibitor of the botulinum neurotoxin light cha...
2011-02-14 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 47(6) , 1713-5, (2011)] |