Rational pathway engineering of type I fatty acid synthase allows the biosynthesis of triacetic acid lactone from D-glucose in vivo.
Wenjuan Zha, Zengyi Shao, John W Frost, Huimin Zhao
文献索引:J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(14) , 4534-5, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Metabolic pathway engineering is a powerful tool to synthesize structurally diverse and complex chemicals via genetic manipulation of multistep catalytic systems involved in cell metabolism. Here, we report the rational design of a fatty acid biosynthetic pathway, Brevibacterium ammoniagenes fatty acid synthase B (FAS-B), that allows the microbial synthesis of triacetic acid lactone (TAL) from an inexpensive feedstock, d-glucose. TAL can be chemically converted to phloroglucinol, which is a core structure for the synthesis of various high value bioactive compounds and energetic compounds such as 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TATB). Synthesis of phloroglucinol from d-glucose using this combined biological and chemical synthesis may offer significant advantages over the current phloroglucinol manufacture, including environmental friendliness and reduction in the cost of phloroglucinol. More importantly, it represents a novel strategy for the benzene-free synthesis of aromatic chemicals.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
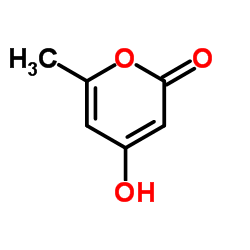 |
6-甲基-4-羟基-2-吡喃酮
CAS:675-10-5 |
C6H6O3 |
|
Purification and properties of 6-methylsalicylic acid syntha...
1992-12-15 [Biochem. J. 288 ( Pt 3) , 839-46, (1992)] |
|
Microbial synthesis of triacetic acid lactone.
2006-03-05 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 93(4) , 727-36, (2006)] |
|
Effect of NADPH-associated keto-reducing domain on substrate...
1996-04-01 [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 328(1) , 213-7, (1996)] |
|
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of...
2008-03-01 [Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 64(Pt 3) , 217-20, (2008)] |
|
Synthesis of acetoacetyl-CoA by bovine mammary fatty acid sy...
1981-09-28 [FEBS Lett. 132(2) , 231-4, (1981)] |