Determination of the insecticide pyridafenthion in river water, soils and wine by adsorptive stripping voltammetry.
M C Sampedro, Z Gomez de Balugera, A Goicolea, R J Barrio
文献索引:Food Addit. Contam. 15(7) , 793-800, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Solid-phase extraction or liquid-liquid extraction has been combined with adsorptive stripping voltammetry at a hanging mercury drop electrode to isolate, determine, quantify and recover trace concentrations of pyridafenthion in water, wine and soil. A systematic study of the experimental parameters affecting the stripping response was carried out by differential pulse voltammetry. By using an accumulation potential of 400 mV and an accumulation time of 540 s, the limit of detection was 0.17 microgram l-1 and the relative standard deviation (n = 10) was 1.9% at a concentration level of 8.5 micrograms l-1. Different methods are proposed which eliminate matrix interferences. These results have been applied to the systematic study of this compound in water, wine and soil. The lowest detectable concentration for pyridafenthion is 34 micrograms l-1 in water, 102 micrograms l-1 in wine and 80 micrograms kg-1 in soil. Recoveries of the pyridafenthion from supplied environmental samples were in all cases higher than 92% with a relative standard deviation lower than 3%.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
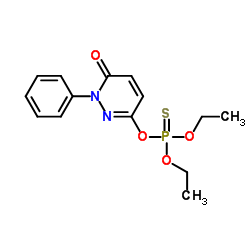 |
哒嗪硫磷
CAS:119-12-0 |
C14H17N2O4PS |
|
[Effects of organophosphorus compounds and PAM on cholineste...
1984-12-01 [Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 39(5) , 795-806, (1984)] |
|
[Effect of ofunack on the tentative exploratory activity of ...
1987-08-01 [Gig. Sanit. (8) , 80-2, (1987)] |
|
[Substantiation of hygienic standardization of ofunak in res...
1988-11-01 [Gig. Sanit. (11) , 66-8, (1988)] |
|
[Evaluation of changes in memory and learning processes caus...
1991-07-01 [Gig. Sanit. (7) , 63-5, (1991)] |
|
Effects of pyridaphenthion on growth of five freshwater spec...
2001-09-01 [Chemosphere 44(8) , 1775-81, (2001)] |