Hypolipidaemic activity of orally administered diphenyl diselenide in Triton WR-1339-induced hyperlipidaemia in mice.
Juliana Trevisan da Rocha, Adriane Sperança, Cristina Wayne Nogueira, Gilson Zeni
文献索引:J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 61(12) , 1673-9, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A significant association between the trace element selenium and hypercholesterolaemia has been reported. This study was designed to investigate a potential hypolipidaemic effect of diphenyl diselenide ((PhSe)(2)) in Triton WR-1339-induced hyperlipidaemia in mice.Triton was administered intraperitoneally (400 mg/kg) to overnight-fasted mice to develop acute hyperlipidaemia. (PhSe)(2) was administered orally (10 mg/kg) 30 min before Triton. At 24 h after Triton injection, blood samples were collected to measure plasma lipid levels. The hepatic thiobarbituric acid reactive substances and ascorbic acid levels as well as catalase and glutathione peroxidase activity were recorded.(PhSe)(2) administration significantly lowered total cholesterol, non-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and triglycerides, whilst it increased high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels in plasma of hyperlipidaemic mice. Neither oxidative stress nor the antioxidant effect of (PhSe)(2) was observed in the mouse liver in this experimental protocol.These findings indicated that (PhSe)(2) was able to lower plasma lipid concentrations. Further studies are needed to elucidate the exact mechanism by which (PhSe)(2) exerted its hypolipidaemic effect in the management of hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
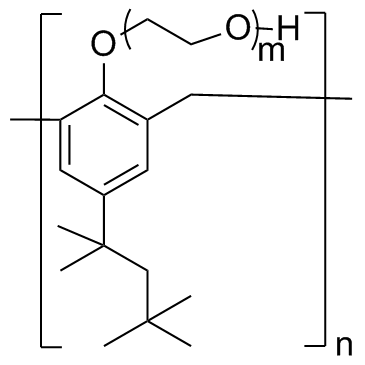 |
四丁酚醇
CAS:25301-02-4 |
(C15H21O(C2H4O)m)n |
|
Filtration improves the performance of a high-throughput scr...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(5) , e96348, (2014)] |
|
The effects of the decaffeination of coffee samples on plate...
2013-09-01 [Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 68(3) , 268-73, (2013)] |
|
Surfactant blocks lipopolysaccharide signaling by inhibiting...
2011-08-01 [Mol. Cell Biochem. 354(1-2) , 113-22, (2011)] |
|
Postprandial changes in high density lipoproteins in rats su...
2013-01-01 [PLoS ONE 8(1) , e55231, (2013)] |
|
In vivo antihyperlipidemic activity of a new series of N-(be...
2012-05-01 [Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 345(5) , 401-6, (2012)] |