| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯酸钾
CAS:3811-04-9 |
|
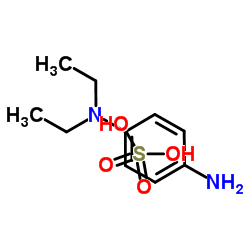 |
N,N-二乙基对苯二胺硫酸盐
CAS:6283-63-2 |
|
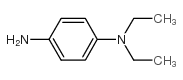 |
N,N-二乙基对苯二胺
CAS:93-05-0 |