Mechanism of reaction of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid with molecular oxygen.
M K Manthey, S G Pyne, R J Truscott
文献索引:Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1034(2) , 207-12, (1990)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The autoxidation of the tryptophan metabolite, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid, at pH 7 gives rise to a p-quinone dimer and cinnabarinic acid. A novel dimer formed by radical-radical coupling of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid is also produced. Labelling studies have shown that the C-2 oxygen in the p-quinone dimer is derived from molecular oxygen. A product versus time study of this reaction has revealed that, in the absence of catalase, cinnabarinic acid is formed but undergoes decomposition by hydrogen peroxide. At pH 7, in the presence of catalase, both the p-quinone dimer and cinnabarinic acid are formed at approximately the same rate and this rate of formation increases with increasing pH. Inclusion of superoxide dismutase was found to increase the rate of formation of cinnabarinic acid, suggesting that superoxide ions may also cause decomposition of cinnabarinic acid. This was confirmed by treating cinnabarinic acid with superoxide. A mechanism involving a common anthranilyl radical intermediate is proposed to account for the formation of the different oxidation products.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
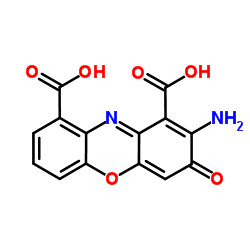 |
朱砂精酸
CAS:606-59-7 |
C14H8N2O6 |
|
Aminophenoxazinones as inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxyge...
2013-04-25 [J. Med. Chem. 56(8) , 3310-7, (2013)] |
|
Simultaneous determination of 3-hydroxyanthranilic and cinna...
1992-02-01 [Anal. Biochem. 200(2) , 273-9, (1992)] |
|
Oxidation of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid to the phenoxazinone ...
1992-09-01 [Biochemistry 31(34) , 8090-7, (1992)] |
|
Oxidative reactivity of the tryptophan metabolites 3-hydroxy...
1987-01-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 36(2) , 211-7, (1987)] |
|
Novel interaction between laccase and cellobiose dehydrogena...
1999-02-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65(2) , 389-95, (1999)] |