Effects of norepinephrine reuptake inhibition on postural tachycardia syndrome.
Elizabeth A Green, Vidya Raj, Cyndya A Shibao, Italo Biaggioni, Bonnie K Black, William D Dupont, David Robertson, Satish R Raj
文献索引:J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2(5) , e000395, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a disorder of chronic orthostatic intolerance accompanied by excessive orthostatic tachycardia. Patients with POTS commonly have comorbid conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, depression, or fibromyalgia that are treated with medications that inhibit the norepinephrine reuptake transporter (NRI). NRI medications can increase sympathetic nervous system tone, which may increase heart rate (HR) and worsen symptoms in POTS patients. We sought to determine whether NRI with atomoxetine increases standing tachycardia or worsens the symptom burden in POTS patients.Patients with POTS (n = 27) underwent an acute drug trial of atomoxetine 40 mg and placebo on separate mornings in a randomized, crossover design. Blood pressure (BP), HR, and symptoms were assessed while seated and after standing prior to and hourly for 4 hours following study drug administration. Atomoxetine significantly increased standing HR compared with placebo (121 ± 17 beats per minute versus 105 ± 15 beats per minute; P = 0.001) in POTS patients, with a trend toward higher standing systolic BP (P = 0.072). Symptom scores worsened with atomoxetine compared to placebo (+4.2 au versus -3.5 au; P = 0.028) from baseline to 2 hours after study drug administration.Norepinephrine reuptake inhibition with atomoxetine acutely increased standing HR and symptom burden in patients with POTS.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
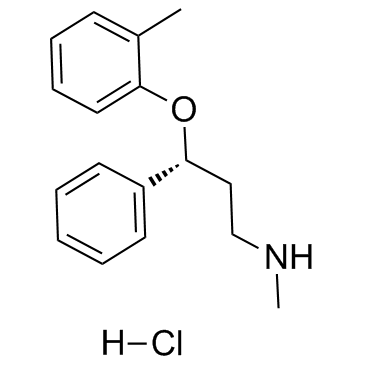 |
盐酸托莫西汀
CAS:82248-59-7 |
C17H22ClNO |
|
Methylphenidate and atomoxetine inhibit social play behavior...
2015-01-07 [J. Neurosci. 35(1) , 161-9, (2015)] |
|
Atomoxetine prevents dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle a...
2014-12-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 351(3) , 663-73, (2014)] |
|
Current pharmacotherapy of attention deficit hyperactivity d...
2013-10-01 [Drugs Today (Barc) 49(10) , 647-65, (2013)] |
|
[ADHD register: post-marketing evaluation of the benefit-ris...
2013-06-01 [Recenti Prog. Med. 104(6) , 254-61, (2013)] |
|
[Life-threatening heart failure caused by ADHD medication. F...
2012-12-01 [Lakartidningen. 109(45) , 2016-8, (2012)] |