Toxic effects of acetochlor on mortality, reproduction and growth of Caenorhabditis elegans and Pristionchus pacificus.
Jingnan Zhang, Wenju Liang, Xia Wu, Siwei Jiang, Qi Li
文献索引:Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 90(3) , 364-8, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effects of acetochlor on the mortality, growth and reproduction of two nematode species were assessed. The LC50 values for Caenorhabditis elegans and Pristionchus pacificus were 1,296 and 210.7 mg/L at 24 h, and 540.0 and 126.4 mg/L at 48 h exposure, respectively. In three succession generations, reproductive capacity was more sensitive in P. pacificus than in C. elegans. Moreover, the sublethal test endpoint of final length was more sensitive with P. pacificus. This study suggested that acetochlor had no long-term effects on C. elegans at lower concentrations. The higher concentrations of acetochlor (from 40 to 160 mg/L) revealed sublethal toxicity to the two tested species, with P. pacificus being more sensitive than C. elegans.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
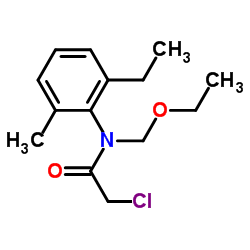 |
乙草胺
CAS:34256-82-1 |
C14H20ClNO2 |
|
Novel three-component Rieske non-heme iron oxygenase system ...
2014-08-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80(16) , 5078-85, (2014)] |
|
Individual and joint toxicity of three chloroacetanilide her...
2013-03-01 [Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 90(3) , 344-50, (2013)] |
|
Assessment of dermal exposure to pesticide residues during r...
2011-05-15 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(10) , 4609-15, (2011)] |
|
Vertical small scale variations of sorption and mineralizati...
2011-04-25 [J. Contam. Hydrol. 123(3-4) , 167-77, (2011)] |
|
Mineralization of isoproturon, mecoprop and acetochlor in a ...
2010-11-01 [Chemosphere 81(7) , 823-31, (2010)] |