Wet air oxidation of epoxy acrylate monomer industrial wastewater.
Shaoxia Yang, Zhengqian Liu, Xiaohui Huang, Beiping Zhang
文献索引:J. Hazard. Mater. 178(1-3) , 786-91, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Epoxy acrylate monomer industrial wastewater contained highly concentrated and toxic organic compounds. The wet air oxidation (WAO) and catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO) were used to eliminate pollutants in order to examine the feasibility of the WAO/CWAO as a pre-treatment method for the industrial wastewater. The results showed that in the WAO 63% chemical oxygen demand (COD) and 41% total organic carbon (TOC) removals were achieved and biological oxygen demand (BOD(5))/COD ratio increased from 0.13 to 0.72 after 3h reaction at 250 degrees C, 3.5MPa and the initial concentration of 100g(COD)/L. Among homogenous catalysts (Cu(2+), Fe(2+), Fe(3+) and Mn(2+) salts), Cu(2+) salt exhibited better performance. CuO catalyst was used in the CWAO of the wastewater, COD and TOC conversion were 77 and 54%, and good biodegradability was achieved. The results proved that the CWAO was an effective pre-treatment method for the epoxy acrylate monomer industrial wastewater.Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
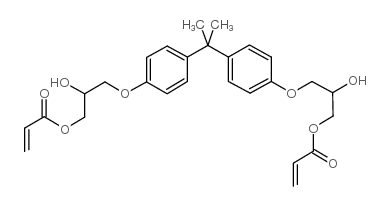 |
双酚A甘油二丙烯酸
CAS:4687-94-9 |
C27H32O8 |
|
Allergic contact dermatitis due to an epoxy acrylate.
1981-06-01 [Br. J. Dermatol. 104(6) , 697-703, (1981)] |
|
The performance of specialized collections of bisphenol A ep...
1993-04-01 [Contact Dermatitis 28(4) , 216-9, (1993)] |
|
The sensitizing potential of di-(meth)acrylates based on bis...
1984-05-01 [Contact Dermatitis 10(5) , 286-304, (1984)] |
|
Sensitization capacity of acrylated prepolymers in ultraviol...
1981-01-01 [Acta Derm. Venereol. 61(1) , 7-10, (1981)] |
|
Occupational dermatoses in workers exposed to epoxy-impregna...
1989-01-01 [Derm. Beruf Umwelt. 37(5) , 171-6, (1989)] |