| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
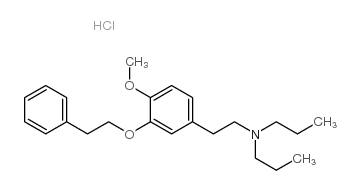 |
NE 100 hydrochloride
CAS:149409-57-4 |
|
 |
(±)-盐酸丁那莫尔
CAS:36504-94-6 |