Neuroprotective effects of sigma-1 receptor agonists against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity.
Agostino Marrazzo, Filippo Caraci, Elisa Trovato Salinaro, Tsung-Ping Su, Agata Copani, Giuseppe Ronsisvalle
文献索引:Neuroreport 16(11) , 1223-6, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Prolonged exposure of cultured cortical neurons to the residue 25-35 fragment of beta-amyloid protein, in the presence of dizocilpine, an antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, and of 6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione, an antagonist of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate receptors, resulted in the expression of the proapoptotic protein Bax and neuronal death. Beta-amyloid protein(25-35)-induced neuronal death was substantially attenuated by the sigma1 receptor agonist 2-(4-morpholinethyl)1-phenylcyclohexanecarboxylate. The neuroprotective action of 2-(4-morpholinethyl)1-phenylcyclohexanecarboxylate was mimicked by the sigma1 ligand methyl (1S,2R)-2-[1-adamantyl(methyl)amino]methyl-1-phenylcyclopropanecarboxylate and was antagonized by the sigma1 receptor antagonist N,N-dipropyl-2-[4-methoxy-3-(2-phenylethoxy)-phenyl]-ethylamine monohydrochloride. These results suggest that sigma1 receptor agonists might function as neuroprotectant agents in Alzheimer's disease.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
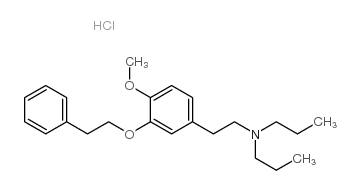 |
NE 100 hydrochloride
CAS:149409-57-4 |
C23H34ClNO2 |
|
Diverse regulation of IP3 and ryanodine receptors by pentazo...
2013-10-15 [Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 305(8) , H1201-12, (2013)] |
|
A sigma-1 receptor antagonist (NE-100) prevents tunicamycin-...
2013-05-17 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 434(4) , 904-9, (2013)] |
|
Prediction of drug-drug interactions for AUCoral of high cle...
2006-02-01 [Curr. Drug Metab. 7(2) , 135-46, (2006)] |
|
Chloroquine inhibits glutamate-induced death of a neuronal c...
2011-11-01 [J. Neurochem. 119(4) , 839-47, (2011)] |
|
A novel adamantane derivative attenuates retinal ischemia-re...
2006-04-24 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 536(1-2) , 200-3, (2006)] |