Pesticides in fermentative processes of wine.
P Cabras, A Angioni, V L Garau, F M Pirisi, G A Farris, G Madau, G Emonti
文献索引:J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(9) , 3854-7, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The influence of six fungicides (azoxystrobin, cyprodinil, fludioxonil, mepanipyrim, pyrimethanil, and tetraconazole) on the fermentative activity of two yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kloeckeraapiculata) and two lactic bacteria (Leuconostoc oenos and Lactobacillus plantarum) was studied. The possibility of their being degraded by these yeasts and bacteria was also investigated. The presence of the pesticides did not affect alcoholic fermentation, not even with levels higher than those normally found in grapes in field experiments. On the contrary, their presence stimulated the yeast, especially K. apiculata, to produce more alcohol. The fermentative process did not affect the amount of pesticides either by degradation or by adsorption. During malolactic fermentation by Le. oenos, malic acid decreased slightly less (by approximately 15%) in the presence of all pesticides, except mepanipyrim. A lower effect ( approximately 5%) was found during the fermentative process with La. plantarum. The bacteria studied did not show a degradative effect on pesticides during malolactic fermentation.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
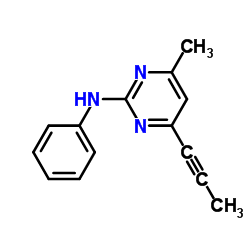 |
嘧菌胺
CAS:110235-47-7 |
C14H13N3 |
|
Gas chromatographic determination of azoxystrobin, fluazinam...
1998-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 81(6) , 1185-9, (1998)] |
|
Evaluation of anilinopyrimidine and other fungicides for con...
2008-07-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 64(7) , 748-54, (2008)] |
|
[Determination of fungicide anilinopyrimidine residues in fo...
2012-09-01 [Se Pu 30(9) , 896-902, (2012)] |
|
Degradation of anilinopyrimidine fungicides photoinduced by ...
2006-09-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 62(9) , 872-9, (2006)] |
|
Effects of mepanipyrim on lipid metabolism in rats.
1998-08-01 [J. Toxicol. Sci. 23(3) , 235-41, (1998)] |