Molecular characterization and expression of microbial inulinase genes.
Guang-Lei Liu, Zhe Chi, Zhen-Ming Chi
文献索引:Crit. Rev. Microbiol 39(2) , 152-65, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Many genes encoding exo- and endo-inulinases from bacteria, yeasts and filamentous fungi have been cloned and characterized. All the inulinases have several conserved motifs, such as WMND(E)PNGL, RDP, EC(V)P, SVEVF, Q and FS(T), which play an important role in inulinase catalysis and substrate binding. However, the exo-inulinases produced by yeasts has no conserved motif SVEVF and the yeasts do not produce any endo-inulinase. Exo- and endo-inulinases found in different microorganisms cluster separately at distant positions from each other. Most of the cloned inulinase genes have been expressed in Yarrowia lipolytica, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris, Klyuveromyces lactis and Escherichia coli, respectively. The recombinant inulinases produced and the engineered hosts using the cloned inulinase genes have many potential applications. Expression of most of the inulinase genes is repressed by glucose and fructose and induced by inulin and sucrose. However, the detailed mechanisms of the repression and induction are still unknown.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
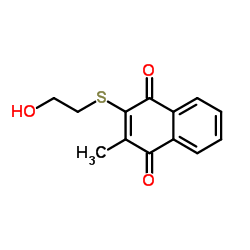 |
菊粉酶 来源于黑曲霉
CAS:9025-67-6 |
C13H12O3S |
|
Ethanol production from inulin and unsterilized meal of Jeru...
2013-11-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 147 , 254-9, (2013)] |
|
First crystal structure of an endo-inulinase, INU2, from Asp...
2012-11-01 [Biochimie 94(11) , 2423-30, (2012)] |
|
Consolidated bioprocessing of highly concentrated Jerusalem ...
2013-10-01 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 110(10) , 2606-15, (2013)] |
|
Expression of family 3 cellulose-binding module (CBM3) as an...
2011-08-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 91(3) , 789-98, (2011)] |
|
Cloning and sequencing of inulinase and β-fructofuranosidase...
2012-04-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78(7) , 2493-5, (2012)] |