| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
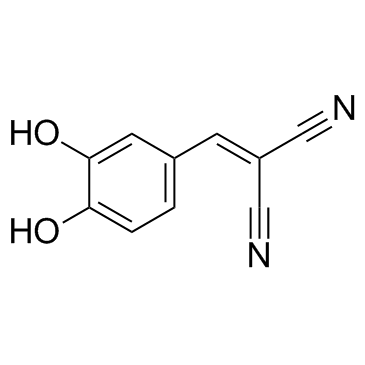 |
(3,4-二羟基苄基)丙二腈
CAS:118409-57-7 |
|
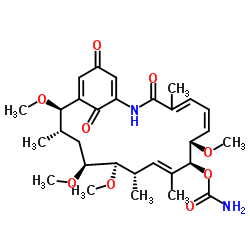 |
除莠霉素A
CAS:70563-58-5 |